In modern agricultural practices, the significance of soil biological activity has become a focal point for achieving sustainable and high-yield farming. Among the various soil conditioners available, humic acid has emerged as a crucial organic compound, promoting soil health by enhancing its biological vitality. This article delves into the profound effects of humic acid on soil biological activity, highlighting its mechanisms, benefits, and applications.
Understanding Humic Acid
Humic acid is an organic compound derived from the decomposition of plant and animal residues over thousands of years. It is rich in carbon and contains functional groups such as carboxylic and phenolic groups, which confer its ability to interact with soil minerals, water, and microorganisms.
Mechanisms of Humic Acid in Boosting Soil Biological Activity
- Stimulating Microbial Growth
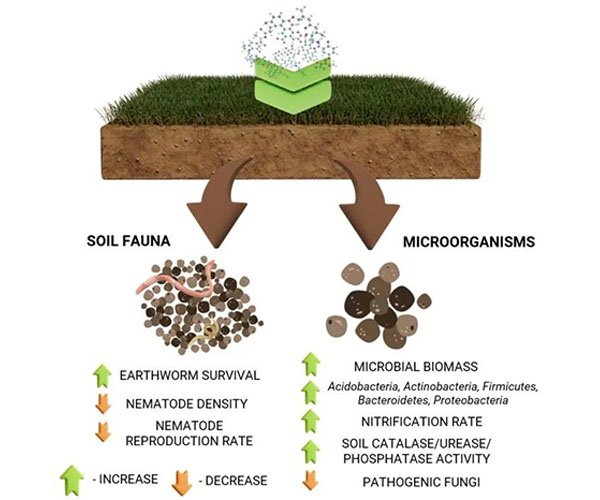
Humic acid serves as a carbon source for soil microorganisms, encouraging their proliferation. Beneficial microbes, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria and phosphate-solubilizing fungi, thrive in humic-acid-rich soils, enhancing nutrient cycling and availability. - Improving Soil Structure
By binding soil particles into stable aggregates, humic acids create an optimal habitat for soil organisms. This improved structure enhances aeration and water retention, supporting the activity of aerobic microbes. - Enhancing Enzyme Activity
It interacts with soil enzymes, stabilizing them and increasing their catalytic efficiency. These enzymes play a critical role in decomposing organic matter and releasing essential nutrients into the soil. - Increasing Nutrient Bioavailability
Humic acid chelates essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese, making them more accessible to plants and microorganisms. This not only improves plant health but also supports microbial activity by providing them with the necessary nutrients. - Detoxifying the Soil
It reduces the toxicity of heavy metals and pollutants in the soil by binding to them, thus creating a safer environment for soil organisms.
Benefits of Enhanced Soil Biological Activity
- Nutrient Cycling
Active soil microbes decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients in forms that are easily absorbed by plants. - Improved Plant Growth
Enhanced microbial activity leads to increased production of plant hormones like auxins and gibberellins, which stimulate root and shoot development. - Disease Suppression
Beneficial microbes supported by humic acid outcompete pathogenic organisms, reducing the incidence of soil-borne diseases. - Resilience Against Environmental Stress
A biologically active soil enhances plant resistance to drought, salinity, and other abiotic stresses by improving root-soil interactions.
Practical Applications of Humic Acid in Agriculture
- Soil Amendment
Humic acids can be applied directly to soils to improve their fertility and structure. It is especially effective in sandy or degraded soils. - Foliar Spraying
When applied to plant leaves, humic acids enhance nutrient uptake and photosynthetic efficiency. - Drip Irrigation
Humic acids can be integrated into irrigation systems, delivering its benefits directly to the root zone. - Composting Additive
Adding humic acids to compost accelerates the decomposition process and enriches the final compost product with biologically active components.
The application of humic acid represents a sustainable approach to improving soil biological activity. By fostering a vibrant soil ecosystem, humic acid not only enhances crop productivity but also contributes to long-term soil health. Its diverse mechanisms and benefits make it an indispensable tool for modern agriculture.
For farmers and agricultural professionals seeking to achieve sustainable growth, humic acids offer a scientifically backed solution that aligns with the goals of environmental stewardship and food security.
If you’re interested in integrating humic acids into your soil management practices, feel free to contact us for tailored solutions and product recommendations.