GABA (γ-Aminobutyric Acid) is a naturally occurring non-protein amino acid that plays a vital role as a plant biostimulant and nutrient efficiency enhancer. It regulates photosynthesis, boosts energy metabolism, supports reproductive growth, enhances nutrient uptake, and strengthens plant stress resistance.
1. What is GABA?
γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) is a four-carbon, non-protein amino acid widely recognized for its critical regulatory functions in plant metabolic and physiological processes. In agriculture, GABA is used as a functional additive in specialty fertilizers, helping plants optimize resource use and enhance overall productivity under various growing conditions.
2. How GABA Works in Plants
(1) Enhancing Photosynthesis Efficiency
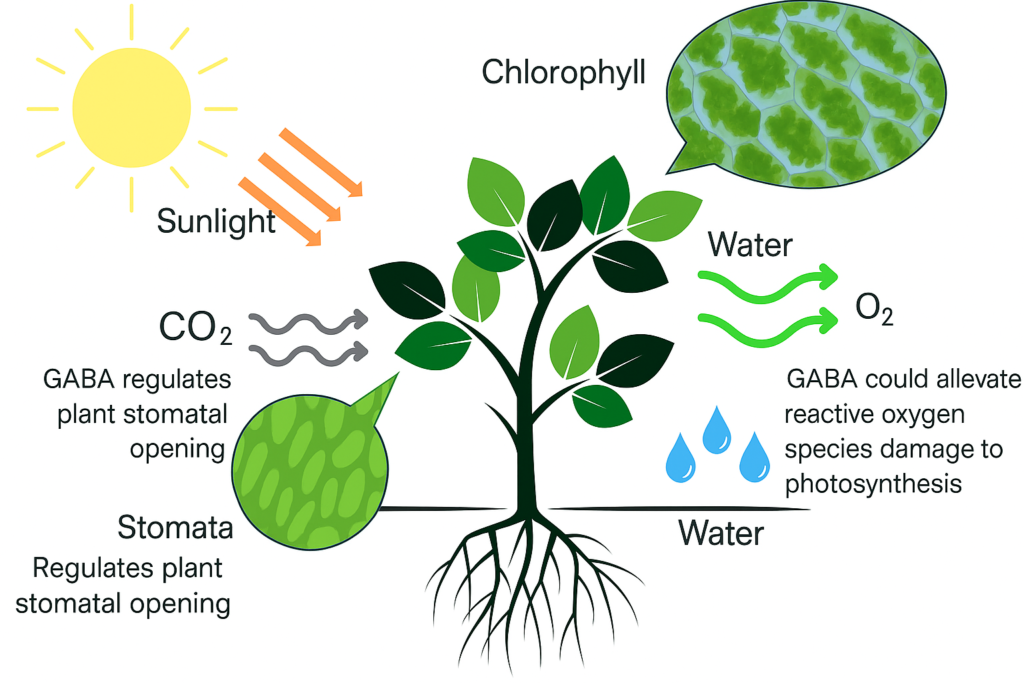
GABA plays an essential role in modulating stomatal opening and closing, thereby regulating the intake of carbon dioxide (CO₂) — a key substrate for photosynthesis. In addition:
- Carbon-Nitrogen Balance: GABA contributes to the redistribution and utilization of carbon and nitrogen, which are vital building blocks in the photosynthetic process.
- Ion Homeostasis: It helps maintain the balance of ions like potassium (K⁺) and calcium (Ca²⁺) within the cell, which is crucial for chloroplast integrity and function, ensuring efficient photosynthetic activity.
(2) Supporting Reproductive Growth
During the reproductive phase, plants demand high levels of energy and biosynthetic precursors. GABA assists in:
- Energy Metabolism Regulation: Optimizing pathways for ATP production and precursor synthesis.
- Tissue Differentiation: Providing the metabolic foundation for cell division, tissue formation, and organ development, which are essential during flowering and fruit setting stages.
3. GABA Boosts Plant Stress Tolerance
Environmental stresses—such as heat, cold, drought, and salinity—significantly affect plant performance. GABA enhances tolerance to abiotic stress by:
- Acting as a cellular signal molecule to trigger stress response pathways;
- Stabilizing cell membrane structures and preventing oxidative damage;
- Modulating hormonal balance under stress conditions (especially ABA and ethylene).
4. GABA Improves Nutrient Uptake Efficiency
GABA promotes more effective nutrient absorption from the soil:
- Increases absorption of Ca, Mg, and B by over 50%;
- Enhances uptake of macronutrients (N, P, K) by more than 20%;
- Improves root activity and membrane permeability, enabling better nutrient transport and assimilation.
5. Application Guidelines
GABA can be applied alone or combined with water-soluble fertilizers and biostimulants for synergistic results.
| Application Method | Recommended Dosage | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Foliar Spray | Dilute 1000 times with clean water | Spray evenly on the foliage during vegetative or reproductive growth stages. |
| Fertigation (drip/flush) | 50g per acre (per application) | Apply with irrigation water. Suitable for all types of crops. |
Note: Frequency of application can be adjusted based on crop cycle, environmental conditions, and stress intensity.
6. Why Choose GABA as Your Fertilizer Enhancer?
- Multi-functional – Combines photosynthesis regulation, energy metabolism, and stress resistance in one solution.
- High Compatibility – Works synergistically with NPK fertilizers, humic acids, trace elements, and other bio-stimulants.
- Scientifically Proven – Backed by multiple trials demonstrating improved plant health and yield quality.
- Safe and Sustainable – Naturally occurring compound with excellent environmental compatibility.
7. Application Scenarios
- Horticultural crops: Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, strawberries
- Field crops: Corn, wheat, rice, soybeans
- Fruit trees: Apples, citrus, grapes
- Turf & ornamentals: Lawns, flowers, green belts
Contact Us
Ready to upgrade your crop management program with GABA?
Let our agronomic team customize a solution for you.
📧 sales@wellyoutech.com | cathyliu@wellyoutech.com
📞 +86 131 3110 5780